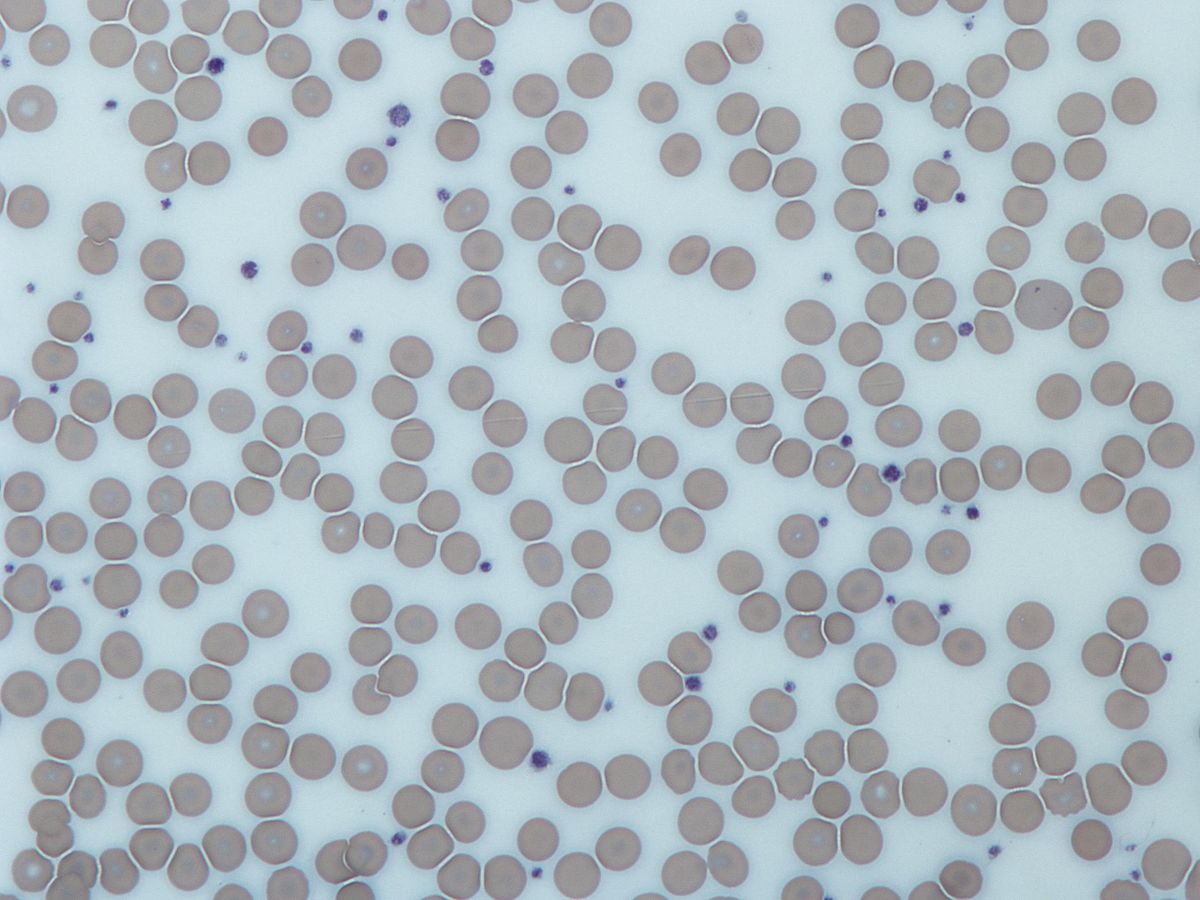
 Platelets or thrombocytes (from Ancient Greek θρόμβος (thrómbos) 'clot' and κύτος (kútos) 'cell') are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a blood clot. [1] .
Platelets or thrombocytes (from Ancient Greek θρόμβος (thrómbos) 'clot' and κύτος (kútos) 'cell') are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a blood clot. [1] ./activated-platelets--artwork-172592952-5a26f99289eacc003739b603.jpg) Platelets help stop bleeding by forming clots, which are essential for healing wounds. A normal platelet count is between 150,000 and 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. Thrombocytopenia, a condition caused by low platelets, can lead to excessive bleeding.
Platelets help stop bleeding by forming clots, which are essential for healing wounds. A normal platelet count is between 150,000 and 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. Thrombocytopenia, a condition caused by low platelets, can lead to excessive bleeding. Platelets, or thrombocytes, are small, colorless cell fragments in our blood that form clots and stop or prevent bleeding. Platelets are made in our bone marrow, the sponge-like tissue inside our bones. Bone marrow contains stem cells that develop into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Platelets, or thrombocytes, are small, colorless cell fragments in our blood that form clots and stop or prevent bleeding. Platelets are made in our bone marrow, the sponge-like tissue inside our bones. Bone marrow contains stem cells that develop into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Overview Thrombocytopenia is low blood platelet count. Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are colorless blood cells that help blood clot. Platelets stop bleeding by clumping together and forming plugs in blood vessel injuries. Thrombocytopenia (throm-boe-sie-toe-PEE-nee-uh) can happen because of conditions or medicines that affect the circulation, production or destruction of blood platelets ...
Overview Thrombocytopenia is low blood platelet count. Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are colorless blood cells that help blood clot. Platelets stop bleeding by clumping together and forming plugs in blood vessel injuries. Thrombocytopenia (throm-boe-sie-toe-PEE-nee-uh) can happen because of conditions or medicines that affect the circulation, production or destruction of blood platelets ...